The mediator acetylcholine: why do humans and other living beings need it? How are acetylcholine and nicotine related? Where is acetylcholine produced and how does it work?
Acetylcholine is one of the main neurotransmitters in the nervous system. But there is very little information about the mediator acetylcholine, written in understandable language. Wikipedia and other sources talk about neurotransmitters with many complex terms that are difficult to understand the first time. In this article we will try to talk about acetylcholine in simple and understandable language.
What are neurotransmitters anyway? Neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry information in the human nervous system. That is, information between nerve structures, in this case, is transmitted not using an electrical impulse, but precisely thanks to special molecules that float in the intercellular fluid. These molecules are called mediators.
We need to immediately tell you about the most important properties of acetylcholine for humans. It directly affects memory and academic performance. The higher the acetylcholine level, the higher they are. And the second important function of the mediator is the process of falling asleep. We fall asleep when we have very little acetylcholine. If you can't sleep, you probably have high acetylcholine levels. This may be due to the fact that you moved a lot or worked at all. We'll tell you why below.
Acetylcholine molecule
Discovery of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter discovered by scientists. And this was done by the German pharmacologist Otto Lewy. In his amazing experiment, acetylcholine stopped a frog's heart.
- Experiment with the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and frog hearts
The scientist took two frog hearts and immersed them in saline solution. And the peculiarity of the frog’s heart is that they can beat for a very long time in a special physiological solution. Then he began to irritate the vagus nerve, which came out of one of the hearts, with an electric current. The heart slowed down its rhythm (this is how it should happen).
After this, the scientist collected some liquid near the heart into a syringe and poured this liquid into the vessel where the second heart was beating. The second heart also slowed down its rhythm.
Otto Lewy's experiment
For the discovery of acetylcholine, and with it neurotransmitters in general, Levy was awarded the Nobel Prize. They say that he dreamed about the experience with frogs at night.
Moreover, the dream was repeated twice; the first time the scientist did not understand what he was dreaming about.
Acetylcholine and nicotine
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is important in the sense that it is its molecule that nicotine copies. In general, almost all drugs are similar in molecular structure to different neurotransmitters.
- Nicotine replaces acetylcholine.
- Opium and heroin copy another neurotransmitter - dopamine, which is also called the “happiness hormone”.
- Ecstasy replaces serotonin, one of the pleasure hormones.
- Alcohol does not replace any mediator with its molecule, but its effect on metabolic processes in the brain is very strong. Alcohol increases dopamine levels, although not as much as opium. Alcohol also complicates the functioning of GABA, a neurotransmitter that is responsible for calmness, concentration and learning. That is, alcohol “turns off the brain” and affects two systems of mediators at once.
There is a drug that blocks cravings for nicotine - Tabex with the active substance cytisine. There is also a more modern drug, Champix, with the active ingredient varenicline. The molecules of these substances connect to acetylcholine receptors in those places where acetylcholine is attached in healthy people or nicotine in smokers. As a result, the craving for nicotine disappears. However, medications are not necessary for those who want to quit smoking; the human body has everything to cope with this problem on its own.
In addition to smoking, there is also chewing, snuff and even sucking tobacco. Nicotine can be absorbed through the skin. This is the basis of the action of nicotine patches. There is also nicotine spray and chewing gum.
The acetylcholine molecule is copied not only by nicotine from tobacco. For example, agonist substances or “substitutes” for acetylcholine are also found in belladonna and dope. The effect of these plants on the human body is even more destructive than that of tobacco.
Datura can cause hallucinations, tachycardia, and photophobia.
But any poison in small dosages becomes a medicine, and preparations from dope and belladonna are used to relieve pain, spasms, to test vision and for some other purposes. For example, the main purpose of the drug Bellastesin is pain relief for stomach ulcers. But you should still be extremely careful with such medications and try to avoid them. In addition to many side effects, they cause persistent addiction.
A drug that duplicates acetylcholine
In general, nicotine and similar substances in plants are toxins. Plants use them as a nerve poison against beetles and other pests that want to feast on them. Nicotine acts like a deadly poison on insects; they are smaller and more vulnerable than humans. Even ripe tomatoes contain small amounts of nicotine; there is a little more of it in tomato leaves and potato leaves. To prevent insects from attacking your garden plants, you can use powdered tobacco. It is also used as a fertilizer.
Main functions
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can be excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptors and the site at which it is released. It can act in different places and perform different functions for the body, being some of the main ones of the following.
Engine control
Voluntary muscle movement requires the action of acetylcholine, which causes the muscle contractions necessary for movement. In this aspect, the functioning of acetylcholine is of an excitatory type, acting through ionotropic receptors.
Activity of the autonomic nervous system
Acetylcholine is one of the main components with which our body can be prepared to act against various stimuli or deactivated after the threat has ceased. This neurotransmitter acts at the preganglionic level, that is, in the transmission of nerve impulses between the medulla oblongata and the ganglion in both the sympathetic system and the parasympathetic system.
In the parasympathetic system, this action also occurs at the postganglionic level between the target organ and the ganglion. In the case of the parasympathetic system, we can observe how the action of acetylcholine has an inhibitory effect. Among other actions, it allows a decrease in heart rate, as well as an increase in intestinal and visceral functioning.
Paradoxical dream
Paradoxical sleep or REM sleep depends on the action of acetylcholine, which is involved in the structure of sleep and gives it various distinctive characteristics.
Article on the topic: “5 stages of sleep: from slow waves to REM sleep”
Hormone production and management
Acetylcholine also has a neuroendocrine function in the pituitary gland, as its action causes an increase in vasopressin synthesis or a decrease in prolactin.
Maybe you're interested in: "Pituitary gland (pituitary gland): connection between neurons and hormones"
5
Awareness, attention and learning. A person's ability to learn through perception is largely mediated by the action of acetylcholine, as well as the fact of maintaining attention and even the level of consciousness
Acetylcholine causes the cerebral cortex to remain active and allow learning
A person's ability to learn through perception is largely mediated by the action of acetylcholine, as well as the fact of maintaining attention and even the level of consciousness. Acetylcholine's reasons are that the cerebral cortex remains active and allows learning.
Formation of memory
Acetylcholine is also a very important substance when it comes to forming memories and tuning our memory, participating in the control of the hippocampus from this area.
Bibliographical links:
Gomez, M. (2012). Psychobiology. CEDE Preparation of manual PIR.12. SEDE: Madrid.
Hall, J. E. & Guyton, A. C. (2006). Textbook of medical physiology. 11th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
Kandel E.R.; Schwartz, JH & Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neurobiology. Fourth edition. McGraw-Hill Interamericana. Madrid.
Katsung B. (2007). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 10th Edition. Mc Graw Hill Medical.
Martin, A. M., & Gonzalez, F. Y. A. (1988). Collection of psychoneuropharmacology. Ediciones Díaz de Santos.
Where is acetylcholine produced?
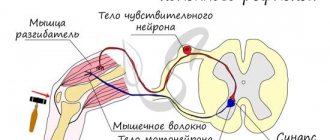
Acetylcholine is produced at neuromuscular junctions near the spine. And it is produced in response to movement, in response to stress, and in general almost constantly. That is, if you decide to move your finger, then signals pass through your nerve fibers. For example, the signal passed from the finger to the spine (the axons or processes of nerve cells are sometimes really so long). In response, a nerve synapse near your spine released the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which caused your finger to bend.
Many conclusions can be drawn from this simple description:
- The simplest conclusion is that active movements and work increase acetylcholine levels and make it difficult to fall asleep.
- Another conclusion is that acetylcholine mobilizes the body. Therefore, if you need to do important work, even mental work, then physical activity will help you.
- Interestingly, acetylcholine is produced not only when you consciously decide to move, but also in nervous and restless individuals. The more anxious a person is, the higher their acetylcholine levels.
- If you decide to quit smoking, then playing sports will make your quitting process faster, but more noticeable. What we don’t use atrophies. And a smoker produces little acetylcholine. If you move a lot, you will put a lot of stress on this system.
Creation and destruction of acetylcholine
Attention receptors
Figure 7. Diversity of acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in the layers of the prefrontal cortex. Drawing from.
For learning, not only intelligence or memory capacity is important, but also attention. Without attention, even the most successful student will fail
Acetylcholine is also involved in processes that regulate attention.
Attention—focused perception or thinking about a problem—is accompanied by increased activity in the prefrontal cortex. Acetylcholine fibers are sent to the frontal cortex from the deep parts of the brain
Due to the fact that we often need a quick switch of attention, it is logical that nicotinic (ionotropic) acetylcholine receptors are involved in the regulation of attention, rather than muscarinic ones, which cause slower and predominantly structural changes in neurons. Damage to acetylcholine structures in the deep parts of the brain reduces the activity of the medial prefrontal cortex and impairs attention. Moreover, the interaction of deep acetylcholine structures with the prefrontal cortex is not limited to ascending signals. Neurons in the frontal cortex also send their signals to underlying regions, which allows for the creation of a self-regulating system for maintaining attention. Attention is maintained due to the effect of acetylcholine on presynaptic and postsynaptic receptors (Fig. 7).
When talking about nicotine receptors and attention, the question arises about improving cognitive functions through smoking, that is, introducing an additional dose of nicotine, albeit in the form of cigarette smoke. The situation here is quite clear, and the results do not give smokers another argument in favor of their addiction. Nicotine that comes from outside disrupts the normal development of the brain, which can lead to attention disorders (for many years). If we compare smokers and non-smokers, the former have worse attention indicators than their opponents. Improved attention in smokers occurs when they smoke a cigarette after a long period of abstinence, when their bad mood and cognitive problems disappear along with the smoke.
Life cycle of acetylcholine
Let's explain some terms in the previous diagram:
Choline acetylase is an enzyme that catalyzes, that is, accelerates and enhances the reaction of the formation of acetylcholine. It is created from two substances acetic acid and choline. Scientists have not yet been able to isolate choline acetylase in its pure form. Its quantity can be judged by indirect signs: the amount of acetylcholine and the rate of its accumulation.
Vitamin B1 , also called thiamine, plays a very important role in the production of choliacetylase . Thiamine, as a medicine, is indicated for use in case of its deficiency, sometimes during pregnancy, heart failure, severe liver disease and other disorders. Thiamine supports processes associated with the functioning of insulin and stimulates the production of the mediator acetylcholine.
Thiamine is available in the form of an injection solution and in tablet form in combination with other B vitamins. These vitamins are indicated for neurological disorders, physical damage to nerve tissue, alcoholism, chemical poisoning and some other conditions.
Thiamine preparation
M and N cholinergic receptors. Receptors are structures that catch a certain substance, in our case the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. It often happens that there is only one mediator, but there are several receptors on which it affects. Acetylcholine acts on nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.
- Nicotinic receptors are found in skeletal muscles and in the autonomic ganglia. The agonist, that is, the substance that replaces acetylcholine in them, is nicotine. These receptors are completely blocked by the deadly snake venom curarine.
- Muscarinic receptors can be found in large numbers in smooth muscle and in the brain. Muscarine, the poison of fly agarics, henbane and other nightshade plants, can replace acetylcholine in them. And poisonous atropine blocks these receptors.
Food
Choline content in different foods:
| Products | % DV for choline |
| 25 g beef liver | 65 |
| 1 boiled egg | 27 |
| 85 g beef tenderloin | 21 |
| 85 g roasted soybeans | 19 |
| 85 g boiled chicken breast | 13 |
| 85 g cod | 13 |
| 75 g oyster mushrooms | 11 |
| 128 g canned green beans | 8 |
| 185 g quinoa | 8 |
| 240 ml 1% milk | 8 |
| 245 g yogurt | 7 |
| 78 g cooked broccoli | 6 |
| 78 g cooked Brussels sprouts | 6 |
Acetylcholine and emotional balance
Smokers know that they need a cigarette to calm down, to cheer up in the morning. Nicotine helps them think about complex problems and, on the contrary, begin active physical work, which does not require much thinking. plays the same role in the human body .
Interestingly, in addition to chemicals, genes also influence the production of acetylcholine. Someone got enzymes and synapses that provide them with a large amount of acetylcholine. And some people have relatively little of this neurotransmitter. Skewing in one direction or the other is not very good.
- With an excess of acetylcholine, a person has excellent memory and a lively mind. But at the same time, he cannot calm down quickly; he is tormented by insomnia.
- With a lack of acetylcholine, a person is calmer and more restrained. But it may seem that he lacks mental agility and speed of reaction.
Acetylcholine levels depend not only on genes. Lifestyle plays a role. Especially physical activity. Psychological attitudes, especially anxiety and severe stress, also play an important role.
Acetylcholine performs the same role as motor oil in an engine
Examples of additives
There is a fairly wide selection of nutritional supplements containing choline in pharmacies and online stores:
| Brand | Description | price, rub. |
| Jarrow Formulas, Citicoline, CDP Choline | Contains 250 mg of citicoline, 120 capsules, it is recommended to take 1 capsule 2 times a day. It is not recommended to take the supplement during pregnancy, planning pregnancy, breastfeeding, or while taking medications. | 2770 |
| Country Life, Choline 100 tablets | Contains choline bitartrate 293 mg per tablet. It is recommended to take 1 tablet per day. | 1013 |
| Solgar, Choline 350 mg | 100 capsules, 1 capsule contains 350 mg choline bitartrate. The recommended daily dose is 1 to 3 capsules per day. | 983.5 |
| Jarrow Formulas, Alpha GPC | 60 vegetable capsules containing 300 mg alpha-GPC | 1920 |
| Kanonpharma production, Holylin | Produced in Russia, 14 capsules, 1 capsule contains 400 mg of alpha-GPC. | 562 |
| Sotex, Cereton | Produced in Russia, 14 capsules, 400 mg alpha-GPC. | 544 |
Acetylcholine is a very important neurotransmitter. When its level is imbalanced in the body, neurological disorders characteristic of Alzheimer's syndrome or Parkinson's disease occur.
Eating a healthy diet and taking supplements helps you get adequate levels of choline, which is converted by enzymes to acetylcholine. Before taking choline supplements, you should consult your doctor to avoid unwanted side effects.
Acetylcholine dopamine and Parkinson's disease
The mediator acetylcholine is difficult to consider without its connections with other mediators. An example of the improper interaction between acetylcholine and dopamine is the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Parkinson's disease is a currently incurable disease that occurs primarily in old age. Although early parkinsonism also occurs from the age of 30. A characteristic feature of such patients is constant trembling of the limbs and difficulties in coordinating movements. Even sitting on a chair or climbing stairs is a problem for such people.
The cause of Parkinson's disease is the depletion and death of cells in the brain that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine. As a result, great difficulty arises in sending a conscious impulse to the muscles, and control over the body is weakened. But the activity of the mediator acetylcholine remains the same. The result is the trembling characteristic of Parkinson's disease.
They try to smooth out this condition using various methods: by blocking the synthesis of acetylcholine or artificially increasing the level of dopamine. But all these drugs are serious and have many side effects. For example, the activity of acetylcholine is reduced by cyclodol, and dopamine is increased by levadopa.
In Alzheimer's disease, which also occurs in old people, acetylcholine, on the contrary, is not enough. And drugs that increase acetylcholine are used for them. These drugs help fight dementia and memory loss in the elderly.
Parkinson's disease
Mediator acetylcholine and VSD
The diseases that we wrote about above, parkinsonism and Alzheimer's disease, are poorly understood and require further research. Another mysterious disease that, in our opinion, is associated with the mediator acetylcholine is VSD or vegetative-vascular dystonia.
the diagnosis of VSD very often. According to various sources, this disorder affects from 25 to 70 percent of people. VSD occurs especially often during hormonal changes in adolescents or in women during menopause.
There is an opinion that VSD is a disease that occurs due to the fact that a person’s “needs” and “wants” do not coincide. For example, you are traveling on a trolleybus and are very tired. You relax in the seat and almost fall asleep, but the next second you remember that people are looking at you and force yourself to wake up. This is repeated several times. The balance of neurotransmitters and vascular tone changes. It's tiring. As a result, hypertension may occur or, on the contrary, blood pressure may drop.
Acetylcholine is an important part of the autonomic system. According to the results of recent Russian studies, stress (which is considered the main cause of VSD) causes the release of large amounts of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is considered a resting neurotransmitter, but after extreme arousal or stress, much more of it is released than usual. If the compensatory systems do not cope and some kind of imbalance occurs in the autonomic system, then this leads to the well-known symptoms of VSD. However, there are now more questions than answers regarding the acetylcholine mediator and the connections between the autonomic and nervous systems.
You may be interested in other articles on our website about hormones and neurotransmitters:
- What is dopamine?
- 5 hormones of joy, happiness and pleasure.
- High and low estrogen in women.
- Oxytocin is the hormone of attachment and pregnancy.
- Adrenaline mediator and medical drug.
Why is there a shortage?
There are several reasons for decreased acetylcholine levels. One possible reason is the presence of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors, for example, in a disease such as myasthenia gravis. There is also evidence that autoimmune reactions to acetylcholine receptors occur in schizophrenia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Insulin resistance and diabetes affect acetylcholine synthesis. But the 2 main causes of acetylcholine deficiency are inappropriate nutrition and medications.
Low fat and vegetarian diets are the main cause of acetylcholine deficiency. Acetylcholine is synthesized from choline, a nutrient belonging to the B vitamins. 90% of people do not get enough choline from food. The foods richest in choline are egg yolks and organic meat. But any fatty animal food contains choline.
Only a few types of plants contain choline in plant foods, and it is almost impossible to get enough choline from vegetarian foods alone.
So, one egg contains 150 mg of choline. The same amount of acetylcholine can be obtained from plant foods by eating 2 servings of tofu, 3 potatoes, 1.5-2 servings of broccoli or 6 servings of brown rice. Therefore, a diet that does not include fatty meats or eggs leads to a lack of choline.
The second main cause of choline deficiency is the use of anticholinergic drugs that block the action of acetylcholine.
Such means include:
- antacids;
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- antidepressants.
Acetylcholine, which plays an important role in the body, is found in anticholinergic drugs, most of which are prescription drugs.
A number of drugs are sold without prescriptions, such as the antihistamine Benadryl and the acid reducer Pepcid AC. Uncontrolled use of these anticholinergic drugs in older people increases the risk of developing dementia. To increase acetylcholine, you may need to eat a high-fat diet, limit your intake of anticholinergics, or take choline supplements.