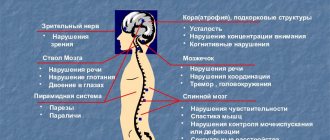
Cerebellar syndrome or cerebellar ataxia is a condition that is caused by a disruption in the functioning of the brain region of the same name. In such cases, movement coordination disorder always occurs.
A pathological process occurs in the cerebellum, in which different parts and areas of this part of the brain suffer. Depending on the nature of the course (static or developing), vestibulo-cerebellar syndrome can be acutely expressed or proceed almost unnoticed.
Damage to the cerebellum as a consequence of the disease
Most often, cerebellar syndrome is a consequence of one or another disease.
This condition can be caused by: ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, damage to the cerebellum in this case occurs due to insufficient nutrition of brain cells, because a stroke involves embolism and occlusion of the arteries;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Guillain's syndrome;
TBI can cause damage to the cerebellum - diseases of the endocrine system;
- obstructive hydrocephalus.
Traumatic brain injury can also become a catalyst for the development of acute ataxia, since due to the injury, parts of the brain may experience pressure from the resulting hematoma.
Even the bite of an encephalitis tick can lead to a serious coordination disorder, which is caused by the manifestation of cerebellar syndrome and related disorders.
Asthenia - symptoms and treatment
Which doctor treats asthenia
The diagnosis of asthenia is considered outdated.
Most often it accompanies another disease and is treated as part of the underlying disease. If symptoms such as weakness, lethargy, and fatigue appear, you should consult a therapist or general practitioner. He will prescribe the necessary examinations and, if the underlying disease that caused the asthenia is identified, he will refer you to a specialized specialist.
When a headache occurs, weakness in the arms and legs, sensitivity, coordination and muscle tone are impaired, it is better to consult a neurologist.
If asthenia develops due to stress, psychological trauma, anxiety or depression, consultation with a psychotherapist or psychiatrist is required.
If you have a chronic disease or cancer, you should contact your doctor, for example an oncologist or cardiologist, since asthenia in this case may be a marker of exacerbation of the disease or tumor relapse.
History taking
The diagnosis of asthenia is made based on symptoms. Therefore, during the consultation, it is important to tell the doctor about your mood, quality of sleep, problems with work and usual activities. The doctor will assess the mental and emotional state, clarify the conditions in which the patient lives, what his daily routine is, whether there are problems in the family or at work, what illnesses he has suffered, whether there have been operations, injuries, etc.
Due to the subjectivity of symptoms, diagnosis is carried out using a variety of tests and questionnaires, for example:
- SAN scale - assesses well-being, activity and mood;
- multidimensional fatigue questionnaire MFI - assesses general fatigue, physical and mental fatigue, decreased motivation and activity;
- Chalder's one-dimensional scale - determines the degree of fatigue.
Also informative are the questionnaire for diagnosing psychological maladaptation by O. N. Rodina and the multi-level personal questionnaire “Adaptability” by A. G. Maklakov and S. V. Chermyanin [2][5].
Tables with all the signs of asthenia have proven themselves well. They help the doctor reduce the interview time, and the patient not to miss all the symptoms that bother him.
Questionnaires are also used to assess associated symptoms such as pain, sleep disturbance, tension, irritability, and mood swings:
- list of symptoms (CDC Symptom Inventory);
- pain questionnaire, or comprehensive pain questionnaire (CPI);
- visual analogue pain scale (VAS);
- Beck and Hamilton test;
- vegetative questionnaire;
- sleepy questionnaire.
To objectively assess mental and physical fatigue, sleep disturbance, personality changes, immune changes, problems of the cardiovascular system and emotional and motivational processes, the following are used:
- Bourdon and Schulte test, memory curve;
- test for level of aspiration, monotony and motor planning.
In addition to those listed, there are many other tests and their variations, they are constantly being improved. Only a doctor can select the necessary and most relevant test.
Instrumental and laboratory diagnostics
There are no special examinations confirming the diagnosis of asthenia. But in order to exclude a somatic cause of the disease, it is necessary to undergo instrumental and laboratory tests.
Clinical assessment of patients with the leading complaint of chronic fatigue requires:
- clarify your medical history, including medications used;
- conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of somatic, neurological, cognitive and mental status;
- do a general and biochemical blood test, a thyroid hormone test and a urine test.
Additional examination usually includes:
- blood test for C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation), rheumatoid factor and creatine phosphokinase (a muscle enzyme);
- tests that confirm infectious diseases, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- examination of the cardiovascular system (ECG, bicycle ergometry, Holter monitoring and ultrasound of the heart);
- neuroimaging (MRI of the brain);
- polysomnography to exclude sleep apnea;
- electroneuromyography to detect abnormalities in neuromuscular transmission characteristic of myasthenia gravis;
- immunological tests.
Additionally, consultation with a specialist, such as a cardiologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist or endocrinologist, may be required.
Differential diagnosis
First of all, it is important to distinguish asthenia from overwork.
| OVERWORK | ASTHENIA |
| Temporary physiological phenomenon | Constant pathological process |
| Occurs due to depletion of energy reserves after intense or prolonged stress | Develops due to problems with energy expenditure, not always related to tension |
| Symptoms disappear after rest | Symptoms do not go away even after vacation |
| No need to see a doctor | Requires treatment as symptoms become chronic, irrational and poorly reversible |
It is also necessary to differentiate asthenia from hypersomnia (daytime sleepiness), hypochondriacal and depressive neurosis.
It is important to distinguish asthenic syndrome against the background of cancer from Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LEMS). This rare autoimmune disorder is accompanied by weakness of the muscles of the trunk, hips and buttocks, problems with articulation, blurred vision, symptoms of sensory polyneuropathy and progressive autonomic dysfunction: wasting of the muscles of the arms and legs, decreased reflexes, numbness and crawling.
With tumors of the thymus gland, myasthenia gravis occurs, which is manifested by increased fatigue and progressive weakness of the affected muscles during exercise. In addition to the clinical picture, an important diagnostic criterion is the result of electroneuromyography (ENMG).
With tumors of the hypothalamic-pituitary zone, panasthenia occurs in the form of an attack of general muscle weakness against the background of hypothalamic epilepsy. The diagnosis can be confirmed with an MRI of the brain and an electroencephalogram (EEG).
Other reasons for the development of the disorder
In some cases, cerebellar damage is not a consequence, but a symptom. This applies to oncological diseases of the following organs and systems:
- lungs;
- brain;
- ovaries;
- lymph nodes.
The “first bell” of brain cancer can be cerebellopontine angle syndrome. As a result of the growth of a malignant tumor, parts of the brain are compressed and nutrition and neural communication in their cells are disrupted.
With prolonged alcohol dependence, substance abuse and drug addiction, irreversible damage to the cerebellum occurs. Ataxia can also become a hereditary disease. In this case, therapy must be selected in a special way.
What is the cerebellum, its functions and structure:
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at reducing the risk of ischemia. A prerequisite is giving up bad habits.
For prevention, it is necessary to avoid stress and reduce the duration of exposure to the sun. Physical activity should be moderate, but constant. One of the necessary preventive measures to prevent this pathology is the regulation of the patient’s body weight, because obesity directly affects the development of vestibular ataxia.
What does it look like - a set of symptoms
Pronounced visible symptoms allow a person to “sound the alarm” and consult a specialist. Timely diagnosis will allow us to determine the exact cause of the disease and the extent of the damage.
Common symptoms include:
- intentional trembling of fingers and hands;
- "drunk" gait;
- asynergia (inability to perform combined movements);
- adiadochokinesis (inability to perform alternating rapid movements);
- nystagmus (high frequency oscillatory eye movements);
- hypotonicity of arm muscles;
- difficulty speaking with division into syllables;
- change in handwriting.
The manifestation of these symptoms may be mild. A rapid disturbance of gait and speech is typical only in cases of traumatic brain injury, when damage to the cerebellum occurs abruptly.
For diagnosis, a specialist may prescribe magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck. This diagnostic method is currently the most common and accurate.
Asthenia: treatment and diagnosis
Since asthenic syndrome usually occurs against the background of various diseases, it is important to undergo a whole cycle of various diagnostic procedures. The specialist can prescribe a complete blood test, urine test, ECG, video EEG monitoring, MRI, ultrasound and other examination methods. This will help the doctor prescribe effective treatment.
Asthenic syndrome that lasts a long time will not go away on its own. Frequent colds and exacerbations of chronic diseases, a feeling of constant persistent fatigue are reasons to pay attention and listen to your body. It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner, without waiting for the disease to progress to a more severe stage, fraught with complications.
Treatment with medications
Depending on the nature of the factors that provoked the disease, a specialist may prescribe medications from various groups.
- Psychotropic drugs. They affect higher nervous activity.
- Vitamin complexes. They replenish the lack of nutrients, increase immunity, and restore metabolism.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Relieves pain in the head, joints and muscles.
- Antiviral drugs. Prevents the spread of viruses in the body.
- Sedatives. Reduce emotional stress.
- Vascular medications. Helps improve blood circulation in the brain.
- Nootropics. They help with weakness and stimulate mental activity.
Other procedures
- Physiotherapy. Special exercises eliminate muscle tension and tone the body as a whole.
- Massage. Helps relax muscles, relieves tension, improves blood circulation.
- Psychotherapeutic techniques. Treatment is complemented by sessions with a specialist, training in breathing practices and relaxation methods.
General recommendations
It is worth optimizing your regimen: plan your day wisely, avoiding overload and fatigue, alternate work and rest, spend many hours in the fresh air, and separately include physical activity in your regimen. Particular attention should be paid to rest. Experts recommend getting at least 8 hours of sleep a day.
Equally important is a healthy, nutritious, regular diet. Quality foods and a balanced diet with sufficient consumption of dietary supplements, vitamins and minerals will strengthen your immune system and fill you with energy.
Examination and diagnosis
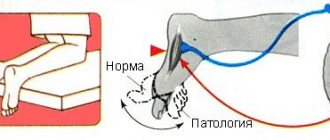
Your doctor may do several tests to look for problems with coordination and ability to move. Static disturbances can immediately catch your eye. The man stands not confidently, not straight.
In order not to fall, he reflexively places his legs at shoulder level, and at the same time one can note a wide amplitude of swing. The body is held slightly tilted back.
During a conversation with a doctor in a standing position, the patient may involuntarily begin to balance with his hands, as he will feel an imbalance. If you move the legs of someone standing, he will simply fall, and he himself will not even notice the fall and will not soften it in any way.
Characteristic manifestations of cerebellar injury
In severe cases, there is a violation of facial expressions. The patient appears to be wearing a mask. Convulsive twitching of the eyes and fingers will leave no doubt that the cerebellum is affected.
Against the background of a pathological process in the brain, the patient may notice deterioration of vision and a depressed emotional background. Psychological distress and major depression may occur. Against the background of these phenomena, the disease will only get worse.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the neurologist will prescribe Dopplerography of blood vessels and MRI of the brain. This will make it possible to clarify the severity of the disease and, in some cases, immediately determine the cause of its occurrence.
Treatment
It is recommended to take antihypertensive drugs, as well as drugs that help lower cholesterol. The person is given advice on changing his lifestyle and is prescribed a special diet. A prerequisite is to quit smoking.
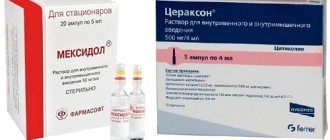
To regulate the blood supply and functioning of the nervous system, as well as relieve symptoms, the use of antioxidants is indicated - Actovegin, Mildronate, Mexidol. Recommended drugs include Cavinton, Instenon and Trental.
For ischemia, symptomatic therapy includes antidepressants, usually of the benzodiazepine type. Among them, Grandaxin has the least number of side effects.
Neurologists who treat patients during rehabilitation procedures usually include physiotherapeutic procedures in their treatment.
In some cases, specialists resort to surgery for therapy. In this case, the operation is performed on the vertebral artery, at the intersection of the vasomotor fibers. This intervention helps to reduce spasms in the arteries and improve blood flow.
Physiatry requires daily monitoring of blood pressure and blood tests for cholesterol levels.