Memory in psychology is an accumulation of certain processes directly responsible for storage, accumulation, and, if necessary, reproduction of various types of information structures. Emotional memory is the accumulation and reproduction of experienced emotional experience, which is tightly “fused” in the psyche with the specific event that caused the emotion.
How to manage this type of memory, develop and strengthen this ability? What are the functions of memory for feelings and emotions. Without the ability to remember traumatic experiences, a person would not be able to fully develop.
Types of memory: emotional memory
The famous psychologist P. P. Blonsky identified 4 main types of memory. The basis for dividing memory into motor, emotional, figurative and logical is which mental activity is more clearly expressed in the process of memorization. So, memory happens:
- Motor - remembering movements. Cycling, skating, knitting - all this is possible thanks to the work of motor, or otherwise, motor memory.
- Emotional - the ability to remember feelings and emotions associated with an object, event or phenomenon.
- Figurative - memory for images of nature, auditory or taste images, or conceptual constants formed in the form of an abstract image.
- Verbal-logical. Memorizing mental images, concepts embedded in words and connections between concepts. It develops when the child can already perceive abstract categories.
Memory of the verbal-logical type is the most complex and develops later than other types, thanks to volitional efforts. If logical memory is well developed, then in an adult it becomes leading in all mental activity. Then a person can direct and control all processes of memorization and reproduction.
As for emotional memory, it is this process that plays a key role in the formation of a socialized personality. It is impossible to make decisions about your future activities without relying on your internal states. Without remembering emotional states, a person would not be able to learn from his mistakes.
Mechanisms of action
According to Blonsky, the initially experienced emotion is brighter than when it emerges from memory. Over time, the emotion becomes dull and mixed with intellectual reflections and other emotions. At the same time, when confronted with similar stimuli or associations, a person’s emotions and feelings come to life, which, during a vivid emotional experience, become what is called a painful point of human perception. In some cases, this type of experience lasts a lifetime.
Three feelings are most vividly remembered - suffering, surprise and fear.
However, there is a difference. Surprise is remembered as an impression that surprised, and such a feeling itself is not experienced again. Painful experiences and suffering are remembered as a feeling of fear.
For a long time, there have been disagreements among scientists about which type of emotions is remembered better - positive or negative? Western psychologists have proven that positive ones leave a deeper mark. Blonsky reasoned from the opposite point of view. He argued that keeping a negative feeling in the mind for a long time, even in the animal world, helps preserve the population species, which proves its great importance.
Blonsky also spoke about the phenomenon of “transfer” of experienced emotions from one stimulus to similar ones. For example, if a child was bitten by a dog as a child, then, as an adult, such a person is afraid of dogs in principle. According to Blonsky, emotional memory has a significant impact on the formation of character. If a child has experienced any type of traumatic punishment or intense fear, this can lead to the development of a fearful and distrustful personality.
In 1977, American psychologists R. Brown and J. Kulik described vivid memories of certain events or situations that provoked the occurrence of emotional shock, strong feelings, as well as the events accompanying these shocks. This phenomenon in psychology is called “mnemonic photoflash”, which translates as: “memory-insight”, “flash-memory”, “vivid memories”.
Connection with acting
Emotional memory is most in demand in the art of theater and cinema. On stage, an actor deliberately recreates emotional memories in his mind to impress the audience. K.S. Stanislavsky told his students about the need for complete immersion in past emotions and feelings, trying to relive them, while understanding the essence of this emotion, understanding why it arose and how it can be transformed. K.S. Stanislavsky taught to evoke the necessary emotions and feelings at will, so that they were not tied to specific events in the student’s life .
In the acting environment, there are exercises, the essence of which is to remember a brightly emotionally colored event in life and reveal it from the point of view of the motives of actions.
How does emotional memory work?
The work is based on the interaction of several structural elements: emotions themselves, positive or negative, feelings, thoughts and information that stimulates the individual’s thoughts and feelings. They are closely interconnected and it is impossible to separate the components in the stream of consciousness. How do you remember emotions?
An experienced situation or phenomenon leaves a trace in the psyche called an engram. Emotions help us determine how successful our relationships with society are and whether our personal relationships are successful. The stronger the emotion, the brighter and clearer the engram. Then a sudden reminder can awaken this trace in memory and “pull out” all the emotions. However, the strength and quality of the newly reproduced emotions differ from the initial reaction. For example, after several years, an event that was upsetting may already be perceived as a funny incident. This is due to the fact that the mental assessment of the event is already different.
In the process of memorization, generalization of experiences often occurs. This means that the stimulus that caused the experience is eventually combined with other stimuli. Because of this, a person sometimes cannot clearly remember the real reason for his fear.
Olfactory memory
Smell is a great memory stimulant. According to experts, olfactory memory is much stronger than visual and auditory memory. This is due to the peculiarities of the structure of the brain. You've probably caught yourself more than once thinking about how some smell immersed you in memories, while a whole chain of events unfolded before your eyes, or a feeling of pleasant, warm nostalgia arose.
According to scientific research, association with a certain smell helps to better remember information. For example, when preparing for an exam, using an incense stick can increase memory efficiency by 30%. It is enough to remember this scent (if it is not possible to reproduce it in reality).
To train your olfactory memory, do the following simple exercises:
- Try to imagine the smell of orange, rose, chocolate, or your favorite perfume.
- Try to remember objects by smell.
This is interesting: In some cases, memory in patients with amnesia is restored when the association with a certain smell is triggered.
Emotional and figurative types of memory
Human emotional memory is closely interconnected with images. Due to the fact that emotions brighten experienced events and captured patterns, our brain is able to produce new images that did not exist. That is, to create art and poetry.
Images can be visual, olfactory and even gustatory. Emotional images are best remembered by actors and poets. It is for these people that emotional memory is always leading. And just like in any other profession, you need to be able to manage images.
Memory training
Memory needs to be trained, like any human skill. Our brain holds tens, hundreds of times more information than a computer, but to unlock this potential we need to train hard.
Thus, train your memory in different ways, and before you start training, you need to answer several questions:
What type of information do I want to remember?
Information can be of different types: visual, audio, tactile, sensory, emotional.
How much do you need to memorize?
There is a difference between memorizing 1-3 people and memorizing a group of 30 people. Memorizing a small passage of text or an entire book.
For how long will I need this information?
You need to remember a lot of information at once and for a short period of time. fast memory works , short-term, and it stores very little information. It also happens when you need to remember information for a month, a year, or even for the rest of your life, and then long-term memory , which is capable of remembering for a long time without maintaining information in active - fast memory .
How are works of art created? The role of emotional memory
People of creative professions are good at using images. They need to be able to analyze and synthesize images, make analogies and produce new ideas. Without constant attention to these mental processes; to the accumulated emotional experience, the images will be blurry. Accordingly, the actor will not be able to reproduce them clearly enough on stage.
The ability to select a chain of similar images for each image is important. All great geniuses were able to keep in memory many such chains of emotional images, which they then embodied in music or drawing. This can be learned. Another important characteristic of the emotional memory of a creative person is a low threshold of sensitivity. The lower the threshold of emotional sensitivity, the more information about the world and other people a creative person can perceive and embody.
General information
Emotional memory is the memory of vivid, memorable events. It plays an important role in the life of all people. Past and preserved emotions and memories become signals that encourage decisive action or deter those that caused previously negative experiences. Emotional memory is much stronger than its other varieties. In some cases, events that happened long ago leave only sensations, emotions, and impressions in memory.
Emotional memory refers to memories of previously experienced emotions and feelings. Experts to this day do not have a consensus on what is better deposited in the subconscious, positive or negative impressions. Western scientists claim that positive emotions are remembered more strongly, while Russians believe that negative emotions (suffering, anxiety) are much more important for survival.
It cannot be said that if there is no emotional memory, then this is a significant disadvantage, but in many professions, for example, teachers and art workers, it is necessary. The ability to sympathize will also become underdeveloped.
If you do not have this type of memory, you should not despair, since this is only a skill that can be improved through constant training.
Physiological basis of memory
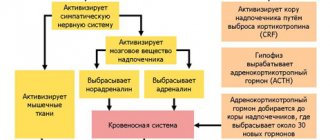
The existence of emotions was confirmed by science when an area called the amygdala was discovered deep in the temporal lobe of the brain. This part of the limbic system is responsible for the emergence of emotions. But vegetative changes in the body under the influence of fear, for example, are the work of the hypothalamus. The processes occurring in the limbic system are both electrical and biochemical in nature; they affect the condition of all organs and systems.
Emotions are therefore always accompanied by activation of the nervous system and changes in blood pressure.
Thanks to the work of the limbic system, a living organism develops using motivation. Behavior is unconsciously either directed to where the person receives reinforcement in the form of positive emotions, or blocked when faced with fear or pain.
All strong emotions are consolidated in memory through the formation of synaptic connections. Various parts of the brain take part in the formation of a memory imprint:
- cerebral cortex: parietal, temporal and frontal;
- the cerebellum is responsible for remembering body movements;
- hippocampus;
- subcortical nodes.
Connections between neurons are not established immediately. The work of chemicals such as endorphins, calcium and enkephalins is important here. These substances are neurotransmitters - hormones that transmit impulses between neurons.
The memorization process requires energy and proteins. Therefore, for a good memory it is necessary to eat well.
Reasons for sudden mood changes
Emotional lability of a person’s personality arises due to many reasons that are individual in nature and can be combined with each other. Physiological reasons - sudden changes in mood in somatic, neurological and mental illnesses. In some cases, lability of emotional reactions appears as a symptom of other diseases:
- neoplasms in the brain;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- encephalopathy - organic brain damage;
- arterial hypertension or hypotension;
- asthenia;
- endocrine pathology.
Psychotraumatic situations and frequent stress are common external causes of lability. Prolonged emotional stress, anxiety, and fears contribute to the development of the disease. Persons with a cyclothymic and demonstrative temperament are at risk. Sharp changes in mood in women and adolescents are often observed due to hormonal changes. In healthy representatives of the fair sex, affective lability (sharp mood swings) is observed in the premenstrual period, which is for the most part the norm.
Types of emotional lability
Impulsive emotional lability includes a symptom of dysphoria - low mood with a feeling of hostility towards others. Patients with this type of disorder, in a fit of rage, are capable of resorting to violence, harming themselves and others. Hot temper is a central characteristic of the impulsive type.
Borderline lability is characterized by increased impressionability and heightened enthusiasm. Patients with this type of disorder have excellent imagination. They are able to become passionate about any activity or person. Sometimes such excessive enthusiasm is not beneficial. Patients are easily suggestible, change interests abruptly, and are restless.
Correction and therapy of emotional lability
The course of treatment for emotional lability is prescribed by specialists, taking into account the causes and individual manifestations of the disease. A full examination is necessary to find out the causes of the pathology. Treatment usually includes psychotherapy, psychotropic medications and general strengthening of the body. Children are treated with mild, natural-based sedatives
It is important for a doctor to confirm or refute the physiological basis of a mental disorder - the presence of neoplasms, organic brain lesions. Among psychotherapeutic techniques, the cognitive-behavioral method is used
Important Basal ganglia
The doctor helps the patient take control of his emotions, redirect them in the right direction, and learn relaxation. Among the medications used for sudden changes in mood are antidepressants or benzodiazepine tranquilizers: Phenazepam, Plevilox, Nozepam, Bifren, Phenibut, etc. Tablets should be used under the strict supervision of a psychotherapist and only after identifying the causes of the disease. Self-administration of medications can harm the body and worsen the situation. If lability is combined with asthenia, general strengthening therapy is prescribed. Necessary:
- allocate more time for rest;
- establish a sleep schedule;
- maintain a proper diet;
- take mild sedatives.
The listed points are what you can do yourself at home to help yourself or a loved one with emotional lability. You can include soothing herbs in your daily diet: lemon balm teas, valerian, a collection of sedative herbs. It is recommended to drink the hot infusion before bedtime. To treat lability, you should consult a psychotherapist.
Development of emotional memory in children and adults
In order for this type of memory to better develop in a child, you need to help him “turn on” more often imaginative thinking, take him to interesting places and accustom him to the world of literature and theater from childhood.
In adults, one type of memory already dominates, and the psyche is aimed at a certain type of activity. It is very difficult for a mature adult to change perceptions and start thinking differently. However, everyone has emotional memory, and you can try to develop it better and bring it to a conscious level.
What tasks need to be performed to develop this type of memory? Emotional memory is trained if every day, while reading a book, you write down on paper the emotions that arise from the actions of one or another character in your favorite book. Then try to analyze the hero’s inner world, conflict situations between him and society. You can also choose a film for such an analysis.
Exercises for children
This type of memory, such as emotional, must be developed from childhood, for which there are special exercises. In childhood, there is an opportunity to build a maximum of positive memories, trust in people and the world, and intellectual potential. Exercises you can do with your children:
- An example of the simplest method: when you are with your child in places where he has not been before, focus his attention on the world around him: trees, views, smells, etc., accompanying this with affection, attention, hugs, so that these memories subsequently give the child strength survive negative events in your life.
- Exercise “I am happy when...”. This exercise is called a group exercise, the technique is used in kindergartens and schools. A ball is thrown to the child asking him to tell about events when he is happy. After this, his task is to perform the same actions in relation to the other.
- An exercise with negative experiences is called the “magic bag”. This technique is usually used by psychologists when a child already has traumatic memories. They find out with the child his painful experiences, grievances, fears, then these emotions are formalized into something tangible, for example - pieces of paper, some objects, and put into a bag that is tightly tied. In parallel with the bag of negative emotions, you can make the same one with positive ones, taking emotions that bring joy in a playful form.
These exercises will help your child increase the number of positive experiences and cope with negativity..
Strive to spend as much time as possible with your child, pay attention to the appearance of his emotional state, hide your negative emotions, because children experience the suffering of their parents more painfully than adults themselves. Walk in new places more often, go on rides, meet animals. Over time, these exercises will give the desired effect in shaping the child’s emotional background.
Parents should remember that they are responsible for most of their children's experiences.
Functions of emotional memory
Why does someone who is not creative need such a memory? The development of emotional memory is necessary for everyone, because a person without emotional experience is uninteresting in communication. In addition, such people are not able to empathize, share painful things and, in essence, are very lonely in their lives. So, we can highlight several functions:
- promotes personality development;
- forms emotional intelligence;
- helps to better navigate society, so it is needed by teachers and company directors;
- influences the development of creativity.
Auditory memory
While studying at school or university, teachers always explain new material.
And the lucky ones are those who perfectly remember the information they listened to. They need less time to prepare homework, since most of the information has already been learned. A reasonable question is how to develop auditory memory in order to make your life and work much easier? Auditory memory training:
- Listen to the conversations of random passers-by, passengers in transport, try to remember the information. At first glance, this seems like an easy task, but if this type of brain function is poorly developed, you will have to try to remember at least something.
- How else to develop auditory memory in an adult? When you hear an unfamiliar voice, try to imagine his portrait without looking at the person. Then compare the result. This exercise not only helps train memory, but also promotes the development of logic, attention, and intuition.
- “Pop music” - turn on a song you know, listen to a short fragment, turn off the sound, continuing to hum the words. Turn on the sound again - does what is playing match what you stopped at?
- It's helpful to listen to your favorite movies and TV shows at a low volume. This exercise trains hearing, attentiveness, and concentration.
- If you like to read, recite the material you read out loud. Or if someone in your family is interested in such an activity, ask him to read aloud, try to remember what he heard. Or you can simply listen to audiobooks while doing household chores.
- Ask someone to clap or tap a simple rhythm and try to repeat it. Start the exercise with 5-7 claps (tapping), gradually making it more difficult.
- Say a few numbers out loud (four at first), repeat them in reverse order. Gradually include two-digit, three-digit numbers, etc. in your number series.
Having mastered simple techniques on how to develop auditory memory for an adult, we move on to the next type.
Emotional intelligence: formation
Emotional intelligence is the ability to understand and control emotions. Without developing emotional intelligence, it is impossible to successfully lead a team. This is an important quality of true leaders.
A person with developed emotional intelligence is easy to recognize. He gets along well with the people around him, as he understands both his own and other people's emotions. He is always friendly and cheerful.
Conclusion
All behavior throughout life is built on the basis of the emotional experience of the individual. The basis for dividing memory into motor and emotional is the mental activity that is more often used by the individual.
The entire limbic system is responsible for maintaining and developing the emotional state. It includes: the amygdala (amygdala), hypothalamus, mastoid body, hippocampus, olfactory triangle, and other structures. Memory is formed through the synthesis of long-term connections between brain neurons.
The ability to create is, first of all, a developed figurative and emotional memory. The development of figurative memory is necessary for those who decide to devote themselves to literary, musical or acting creative activity.
Physiology of the memory process
The ability to retain information is not unique to humans. Animals with a developed central nervous system can also remember and reproduce data (migratory birds know routes). The volume and duration of data storage depends on the number of nerve cells involved in the process.
Information recorded in short-term memory is transferred to long-term memory through a complex biochemical process. The neurons that make up the brain work like a recording device - they remember information and store it. Data is recorded not on individual neurons, but on a neural network - a stable collection of cells.
When a person remembers information, neurons become active. The data travels along the fibers and reaches the cluster. For information seen earlier, there is a ready-made accumulation in the brain. For data that a person learned for the first time, a new neural network is formed. There are connections between networks. A disruption in the functioning of at least one of them leads to the erasure of memories.